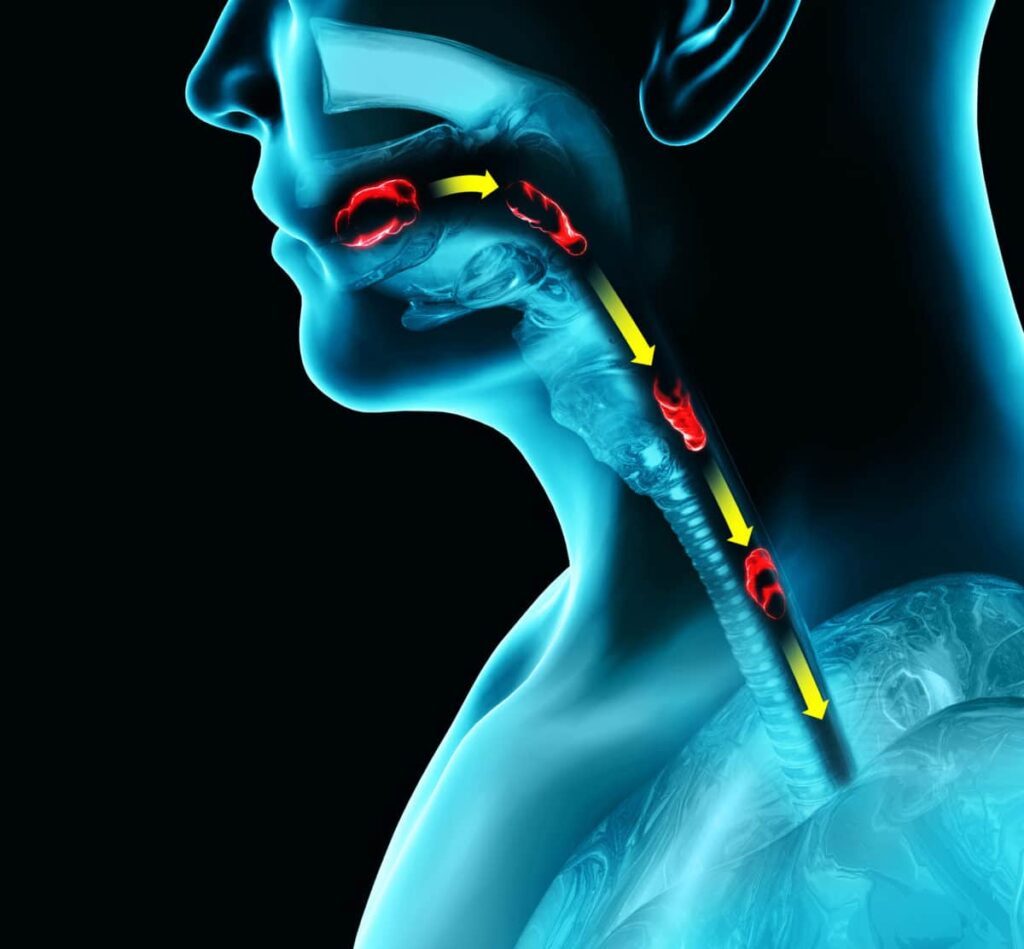
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic immune-mediated disorder that impacts the esophagus, the muscular tube connecting the throat to the stomach. This is a relatively rare condition, only affecting an estimated 1 in every 2,000 people.
In EoE cases, an abnormal accumulation of the white blood cell “eosinophils” occurs in the lining of the esophagus. This triggers inflammation and damage to the esophageal tissue, resulting in a range of symptoms and complications.
Most commonly, EoE is hallmarked by trouble swallowing, chest pain, heartburn, or food getting stuck in the esophagus. For diagnosis, most patients will need to seek an assessment from an allergist and/or gastroenterologist.
What Causes Eosinophilic Esophagitis?
Eosinophilic esophagitis is considered an allergic condition and is associated with other allergic conditions such as asthma, hay fever, and food allergies. The exact cause of EoE is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of factors, including…
Allergies
Because EoE is often associated with allergic conditions, it is believed that exposure to allergens may trigger an immune response in the esophagus. This then contributes to inflammation and the accumulation of eosinophils.
Genetics
EoE tends to run in families, which suggests that there is a genetic component to its development. Researchers have also identified specific genetic variations that may contribute to the risk of EoE, although more information is needed to fully understand the relationship between genes and EoE.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can include exposure to certain allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, and certain foods. EoE may also sometimes be triggered by infections and the use of antibiotics.
Possible Environmental Risk Factors
- Residing in a cold or dry climate that aggravates allergies
- Spending time outdoors in high levels of pollen and other allergens
- Living in a dusty, dirty, or drafty living space
How Common is Eosinophilic Esophagitis?
Eosinophilic esophagitis has been considered somewhat rare since its discovery in the early ‘90s, but its prevalence has been increasing in recent years. It is now recognized as a fairly common cause of chronic esophageal inflammation.
Most cases appear in adults, and the condition is three times more prevalent in men than in women. However, the prevalence of EoE is estimated to have increased in both adults and children in the past two decades.
It’s important to note that the prevalence of EoE will likely continue to evolve as research and awareness of the condition progresses. If you suspect you or someone you know may have EoE, consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis can cause a range of symptoms that primarily affect the esophagus. The effects may vary depending on the age of the individual and the severity of the condition.
The most common symptoms associated with EoE include…
Match with Eosinophilic Esophagitis Clinical Trials
Have you been diagnosed with eosinophilic esophagitis? You may qualify for a clinical trial near you. At Tandem Clinical Research, we’ll help you match with…
- Research groups in your area
- The latest treatments
- Scientific clinical studies
Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
The diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis usually involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging tests, and procedures.
If you have experienced any signs of eosinophilic esophagitis, seek medical attention, especially if you are frequently dealing with food impaction. Most medical providers will take the following steps to confirm a diagnosis.
1. Assess medical history and symptoms
The healthcare provider will first ask for a detailed medical history, then inquire about the symptoms the individual is experiencing. They may also inquire about any known allergies or if there is an existing family history of EoE.
2. Conduct a physical examination
A physical examination may be performed to check for any signs or abnormalities that could be related to EoE. This will likely include assessing the patient’s weight and ability to breathe easily.
3. Schedule an endoscopy
If the patient’s history and physical examination lead the medical provider to believe that EoE is a possibility, they will likely schedule an upper endoscopy, also known as esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD).
This procedure is performed so that the healthcare provider can clearly see the esophagus and take biopsies. A flexible tube with a camera on the end is inserted through the mouth and into the esophagus.
The medical provider will examine the esophageal lining for signs of inflammation, narrowing, or other abnormalities. They may also take multiple tissue samples (biopsies) from various areas of the esophagus for further testing.
4. Analyze tissue samples
Any tissue samples obtained during the endoscopy will be sent to a laboratory for histological analysis. There, a pathologist will examine the samples under a microscope to assess the presence and extent of eosinophils, the white blood cell associated with this particular allergic reaction.
5. Recommend diet changes
Because EoE is often associated with food allergies, further evaluation may involve food allergy testing and eliminating potential trigger ingredients. This will help the healthcare provider and patient identify specific foods that could be causing or exacerbating the condition.
6. Conduct imaging tests
In some cases, the medical provider may request imaging tests like a barium swallow or an upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy to assess the structure and function of the esophagus.
Note that the diagnosis of EoE requires ruling out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or other esophageal disorders.
If you suspect you may have EoE, consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and proper diagnosis.
Treatment for Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) treatments aim to alleviate symptoms, but there are no treatments that can fully cure the condition. In most cases, these solutions primarily reduce esophageal inflammation and help prevent complications.
Remember: it is always important to work closely with a healthcare professional experienced in managing EoE to develop an individualized treatment plan based on your specific needs and circumstances.
Eosinophilic Esophagitis Clinical Trials
If you have been diagnosed with eosinophilic esophagitis, you could be a candidate for clinical studies. These trials allow researchers to obtain valuable information about the condition, which can then influence treatment options.
Scientists and doctors are currently studying many aspects of eosinophilic esophagitis. This includes the assessment of…
- new treatment possibilities
- how genetics and environmental factors increase the risk of EoE
- how the condition develops and progresses
At Tandem Clinical Research, we match patients with trials conducted in hospitals, universities, and research centers. If you’re interested, reach out to learn about the clinical trials in your area.
How to Support Others With Eosinophilic Esophagitis
If your friend or family member has recently been diagnosed with EoE, you are likely wondering how to help them. Here are some of the most important things you can do.
Learn About the Condition
Research eosinophilic esophagitis, as well as its symptoms, treatments, and dietary considerations. This will help you understand the challenges your loved one will face and how best to support them on their journey.
Show Empathy
Eosinophilic esophagitis can be a chronic and sometimes debilitating condition. As your loved one moves forward, try to show empathy and understanding toward their condition. Acknowledge their struggles and offer a listening ear if they need it.
Accommodate Their Diet
Individuals with EoE often have specific dietary restrictions. When hosting your next get-together or sharing meals, try to accommodate their needs as much as you can. If possible, ask about their dietary preferences and restrictions beforehand.
Offer Practical Help
This could involve assisting with meal preparation, grocery shopping for specialized items, or helping them find resources such as dietitians or support groups in their area.
Match with Eosinophilic Esophagitis Clinical Trials
Tandem Clinical Research is here to help you match with reputable clinical trials. If you live near New York City, New Orleans, or Orlando, contact us to find trials conducted by pharmaceutical, biotech, and medical device companies.
We might not currently have a cure for eosinophilic esophagitis, but scientists and doctors are continuously researching potential new treatments. The more we learn about EoE, the better we can become at preventing and treating it.
If you’ve been diagnosed with eosinophilic esophagitis, we invite you to learn more about contributing to ongoing research.