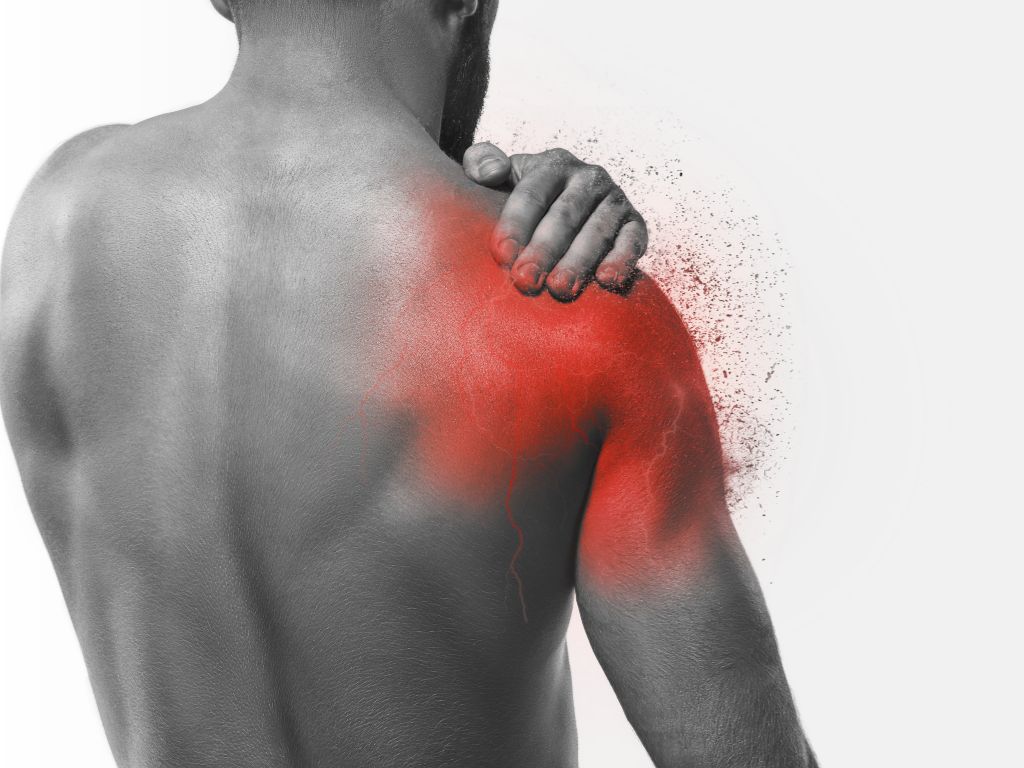
Rotator cuff tendinopathy is a condition in which the rotator cuff muscles in the shoulder are damaged, irritated, or inflamed. Shoulder disorders are relatively common, but this particular condition is considered the most common type of chronic shoulder pain, seen in about 30% of the overall population.
Your rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and their associated tendons that surround the shoulder joint. Their job is to keep you stable and enable various shoulder movements, whether that’s reaching for an object on a shelf or swinging a tennis racket.
Tendinopathy is a general term for conditions affecting tendons and can encompass both tendonitis (inflammation of the tendon) and tendinosis (degeneration of the tendon without significant inflammation).
In the case of rotator cuff tendinopathy, the tendons of the rotator cuff become damaged or degenerate over time, leading to pain, weakness, and limited range of motion in the shoulder. This can be caused by a variety of things, including overuse and aging.
Athletes who engage in sports that involve repetitive overhead motions, such as baseball pitchers or tennis players, may be at an increased risk for this form of tendinopathy.
Symptoms Associated With Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy
Pain
Persistent pain in the shoulder, especially when lifting or reaching overhead, is a hallmark symptom. The pain may also be present when you’re resting, and it can be a sharp or a dull ache. Typically, it worsens during overhead activities or if you sleep on the affected side.
Weakness
Weakening of the affected shoulder muscles can occur. This may manifest as difficulty lifting or carrying objects, as well as a feeling of instability in the shoulder.
Limited Range of Motion
Rotator cuff tendinopathy can lead to a restricted range of motion in the shoulder joint, resulting in difficulty lifting the arm, especially overhead. Individuals may also experience stiffness and tightness, making it challenging to perform everyday activities that involve reaching or rotating the affected shoulder.
Crepitus
This condition may be accompanied by crepitus – a sensation of crackling or grinding within the shoulder joint during movement. This can result from friction between inflamed tendons and surrounding structures, contributing to the overall discomfort and indicating potential degeneration or roughening of the affected tissues.
Note: the severity and combination of symptoms can vary among individuals with rotator cuff tendinopathy. Additionally, symptoms can appear gradually and worsen over time.
If you are experiencing persistent shoulder pain or relate to any of these symptoms, seek attention from a trusted healthcare professional, such as an orthopedic specialist or a physical therapist. They will conduct a thorough examination to diagnose the condition and recommend an appropriate treatment plan.
Early intervention is often key to managing rotator cuff tendinopathy effectively. The sooner you let your healthcare provider know about your symptoms, the sooner you can begin treatment.
The Risks of Living With Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy
Increased Pain and Discomfort
Untreated rotator cuff tendinopathy poses the risk of escalating pain and increased discomfort over time. Without intervention, the condition may progress, leading to further inflammation, impaired shoulder function, and potential degeneration of the affected tendons.
Loss of Function
Over time, the tendinopathy can progress, contributing to weakness and a reduced range of motion in the affected shoulder. This loss of function can impact daily activities, work, and recreational pursuits.
Development of Tears
If left untreated, tendinopathy can progress to more severe conditions, such as partial or complete tears of the rotator cuff tendons. Tears will further exacerbate pain and functional limitations, and they usually require physical therapy, regenerative medicine, and sometimes surgical intervention.
Muscle Atrophy
Chronic inflammation and tendon degeneration may result in decreased use of the affected muscles, causing them to weaken and shrink over time. This muscle atrophy can further contribute to functional impairment, reduced strength, and increased difficulty in performing regular shoulder movements.
Impaired Sleep & Daily Activities
Many people with untreated rotator cuff tendinopathy have trouble sleeping at night. Their pain, aches, and discomfort make it challenging to achieve solid rest, which can impact their overall quality of life, physically and emotionally.
Why Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy Is Challenging to Overcome
What Increases the Risk of Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy?
Rotator cuff tendinopathy can affect individuals of various ages and backgrounds, but certain factors may increase the risk of developing this condition. Some common risk factors include:
Age
The risk of rotator cuff tendinopathy tends to increase with age, primarily affecting patients over the age of 30. The tendons of the rotator cuff can degenerate and change over time, making adults more susceptible to this condition as they get older.
Repetitive Overhead Activities
Engaging in activities that involve repetitive overhead motions or excessive use of the shoulder can increase the likelihood of developing rotator cuff tendinopathy. Athletes such as baseball pitchers, tennis players, and swimmers are especially at risk.
Additionally, individuals in professions that require frequent overhead movements (painters, carpenters, etc.) can be more prone to developing this condition. This makes it challenging to treat the condition, too, unless the patient can significantly alter their daily activities.
Trauma or Injury
Acute injuries or trauma to the shoulder, such as a fall or direct impact, can contribute to the development of rotator cuff tendinopathy. This trauma may lead to inflammation and damage to the tendons.
Biomechanical Factors
Poor shoulder biomechanics or shoulder joint abnormalities can increase the risk of developing rotator cuff tendinopathy. This includes factors such as shoulder impingement syndrome, which occurs when the tendons of the rotator cuff are pinched between the bones of the shoulder.
Muscle Imbalances
Weakness or imbalances in the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint can contribute to the development of tendinopathy. That’s why all patients should prioritize maintaining muscle strength and coordination while also avoiding putting excessive stress on the tendons.
Genetic Predisposition
A genetic component may influence the likelihood of developing rotator cuff tendinopathy. Individuals with a family history of shoulder problems may have an increased risk, although this does not always mean you will deal with tendinopathy.
Systemic Diseases
Certain systemic conditions, such as diabetes and autoimmune disorders, can compromise your body’s blood flow, trigger inflammation, and generally degenerate tendons – including those of the rotator cuff.
Smoking
It’s widely accepted in the medical community that smoking impairs the body’s blood flow and diminishes its ability to repair and maintain connective tissues. Therefore, if you’re a regular smoker, you may be compromising the integrity of your rotator cuff tendons.
Note: While these factors may increase the risk of developing rotator cuff tendinopathy, the condition can still occur in individuals without these specific risk factors.
Additionally, proactive measures such as proper warm-up, conditioning, and maintaining good shoulder mechanics can help reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Match With Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy Clinical Trials
Have you been diagnosed with rotator cuff tendinopathy? Are you experiencing chronic shoulder pain caused by tendon deterioration?
If so, you may qualify for clinical studies to help researchers learn more about rotator cuff tendinopathy and how we treat it. These studies are considered safe for patients and contribute to critical scientific and medical discoveries.
The purpose of these studies may include researching:
- The relationship between genetics, environmental factors, and tendinopathy
- Risk factors for rotator cuff tendinopathy and general shoulder pain
- New treatments for rotator cuff tendinopathy
Participating in these studies benefits both you and future patients. If you’re interested in joining a trial, reach out to us today to learn about opportunities near you.
Potential Treatments for Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy
Physical Therapy
This is the most common form of treatment for rotator cuff tendinopathy and typically involves targeted exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles. Physical therapy also helps:
- Improve flexibility
- Correct movement patterns
- Alleviate pain
- Enhance range of motion
- Restore shoulder tendon function
Some patients can foster long-term recovery through physical therapy and reduce the risk of future shoulder issues.
Medications
In some patient care plans, medications play a role in addressing pain and inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and pain relievers help manage symptoms, facilitating improved function and comfort during rehabilitation and daily activities.
Corticosteroid Injections
These injections can provide targeted relief by reducing inflammation and pain in the shoulder joint. However, corticosteroid injections typically only offer short-term benefits and are used judiciously because of their potential side effects (hormone imbalances, weakened tendons, etc.).
Heat & Ice Therapy
Applying heat to the shoulder can help increase blood flow, promoting healing and relaxation. Conversely, ice reduces inflammation and numbs the area, providing pain relief. Alternating between heat and ice can effectively manage symptoms and aid in the recovery process.
Lifestyle Changes
Big lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and modifying activities that strain the shoulder, can be huge in the treatment of rotator cuff tendinopathy. However, you should always discuss big lifestyle changes with your healthcare provider before starting.
Surgical Interventions
In especially severe cases of rotator cuff tendinopathy, surgery may be recommended. Procedures such as arthroscopic repair or open surgery can help directly address the damaged tendon, restoring function and relieving pain.
How to Support Others With Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy
Considering that rotator cuff conditions affect up to four million Americans every year, one of your loved ones may very well deal with some form of tendinopathy in the future. It can be challenging to know how to support them, but here are some great strategies to help.

Be Empathetic
Understand the pain and limitations associated with rotator cuff tendinopathy. Your friend or family member might need to alter their hobbies or daily activities to help their body heal, and you’ll want to demonstrate empathy and patience as they navigate their condition.

Encourage and Motivate
Chronic conditions are hard to live with and can increase the risk of anxiety and depression. Additionally, recovering from rotator cuff tendinopathy may involve extensive physical therapy and lifestyle changes. During this time, your support can be invaluable to your loved one, even if you’re just offering a shoulder to cry or an ear to listen.
Remember that everyone’s experience with rotator cuff tendinopathy is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. If in doubt, talk to your loved one and ask what they need or want from your support.
Match With Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy Clinical Trials
Tandem Clinical Research specializes in connecting patients with rotator cuff tendinopathy and other health conditions with clinical trials. If you live in or near New York City, New Orleans, or Orlando, we’re here to match you with trials.
Rotator cuff tendinopathy might be a big part of your life right now, but the latest studies are helping to develop new treatments and solutions for patients. Consider joining a clinical trial today to contribute to this critical research.
No post found!