
Headaches and migraines are common ailments that affect millions of people worldwide. While the two may seem similar at first glance, they are distinct conditions with different causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Studies show that around 52% of people have an active headache disorder. Although less common, migraines are still a significant health concern, affecting around 14% of the population.
If you struggle with either of these conditions, this comprehensive blog post will help you learn more about your symptoms and what could be causing them. Let’s delve into the characteristics present in migraines vs headaches so you can learn how to identify and treat them accurately.
Understanding Common Headaches
For many, headaches are all too familiar. In fact, it’s estimated that 96% of people will experience a headache at least once in their lifetime.
Understanding the different types of headaches, their symptoms, and what triggers them can help you manage and prevent them more effectively. There are more than 150 types of headaches, but let’s discuss some of the most common ones.
Types of Headaches
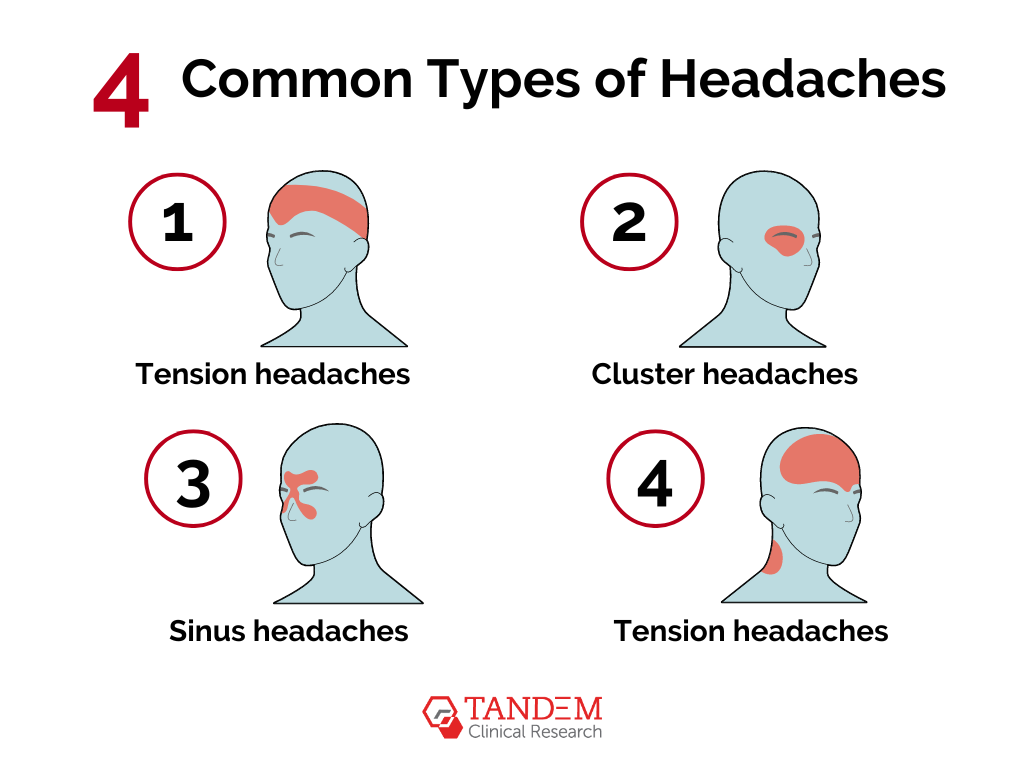
- Tension headaches are usually caused by stress, anxiety, or muscle strain. They’re often described as a feeling of a tight band around the head.
- Cluster headaches are characterized by severe, piercing pain on one side of the head, often around the eye. These occur in groups or clusters over a period of weeks or months.
- Sinus headaches are associated with sinus infections or inflammation. These headaches come with pressure and pain in the forehead, cheeks, and nose.
- Rebound headaches are a type of secondary headache that results from overuse of medications.
Common Symptoms and Triggers of Headaches
There are hundreds of potential causes for headaches, from stress and dehydration to poor posture and lack of sleep. Certain foods, medications, and drinks can also trigger headaches in some people.
If you have one, you’re likely experiencing a dull, aching sensation, pressure around the forehead, or tenderness in the scalp, neck, and shoulder muscles.

Duration and Intensity
The duration of a headache can vary from as short as 30 minutes to a few hours. In some cases, a headache can even last a few days.
The intensity also varies, typically ranging from mild to moderate. Sometimes, it’s just a dull ache that you can push through. Other times, the pain can be more severe, making it difficult to carry out everyday tasks.
What is a Migraine?
If you’ve ever experienced a migraine, you know it’s more than just a bad headache—it can be overwhelming and disrupt your entire day. Let’s explore how migraines manifest and impact daily life.
Common Types of Migraines
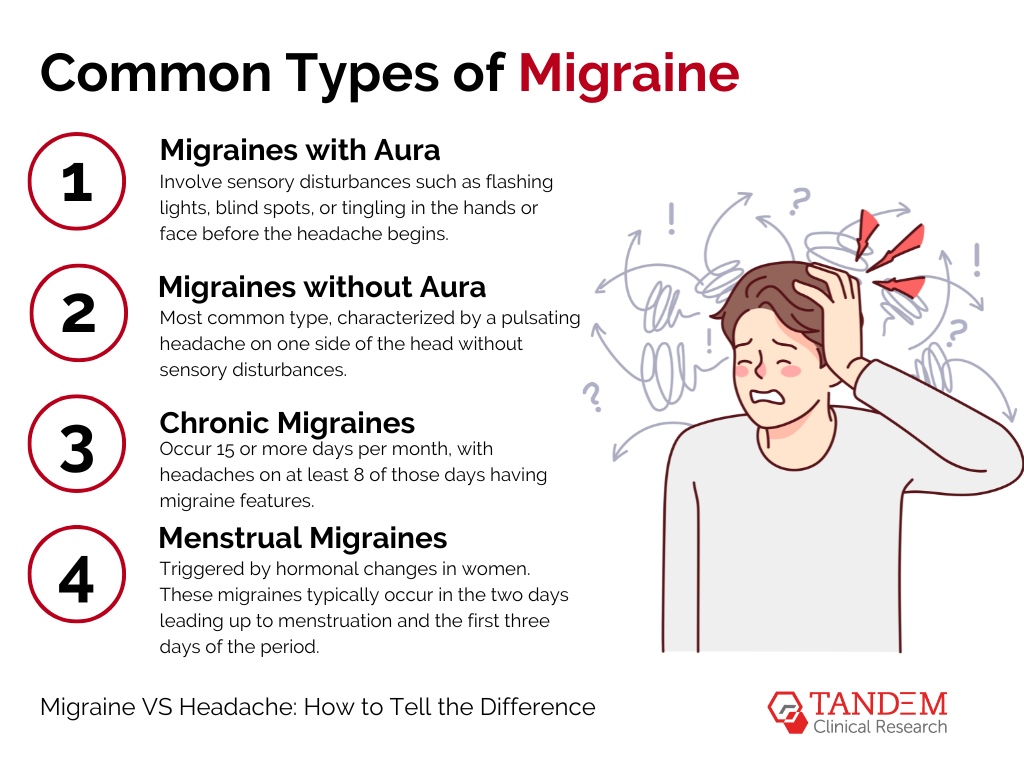
Migraines come in various forms, each with its own unique set of challenges. Here are some of the most common types of migraines:
- Migraines with aura involve sensory disturbances such as flashing lights, blind spots, or tingling in the hands or face before the headache begins.
- Migraines without aura are the most common type, characterized by a pulsating headache on one side of the head without sensory disturbances.
- Chronic Migraines occur 15 or more days per month, with headaches on at least 8 of those days having migraine features.
- Menstrual migraines are triggered by hormonal changes in women. These migraines typically occur in the two days leading up to menstruation and the first three days of the period.
Migraine Symptoms and Triggers
The symptoms of migraines are hard to miss. According to the Mayo Clinic, migraines begin with a prodrome period of one or two days. During this time, you may notice symptoms like food cravings, fluid retention, constipation, and more.
Migraine attacks are often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and extreme sensitivity to light, sound, or smells. It’s like your senses go into overdrive, and even the faintest light or softest sound can feel unbearable.
As with headaches, the cause of migraines is largely unknown and can include many complex factors. Migraine triggers can include hormonal changes, certain foods and drinks, stress, sensory stimuli, and changes in sleep patterns.
Duration and Intensity

The duration of migraine attacks can vary. Typically, migraines can last from 4 hours to 72 hours if untreated.
According to The International Headache Society, chronic migraines are characterized by experiencing 15 or more headaches and migraines each month for at least three months.
During a migraine attack, the intensity of the pain can escalate. Extremely intense migraines make it difficult to perform even the simplest tasks.
The pain is often described as throbbing or pulsating and typically affects one side of the head, although it can sometimes spread to both sides.
Key Differences Between Migraines and Headaches
When it comes to understanding migraines vs headaches, it’s crucial to learn more about how – each one works.
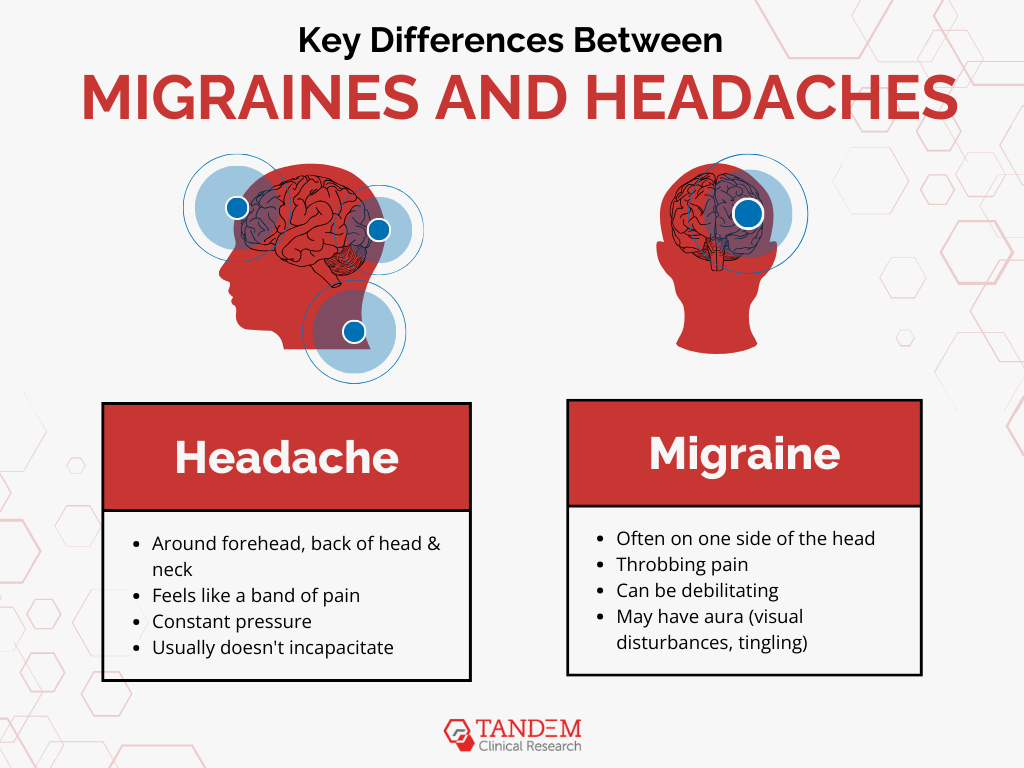
1. Location and Intensity
Headaches, particularly tension headaches, are often described as a band of pain around the forehead or the back of the head and neck. This type of pain is usually diffuse and can feel like a constant pressure or tightness.
Migraines, however, are usually unilateral, affecting one side of the head with a throbbing or pulsating pain. This intense, localized pain can often radiate to the temples or behind the eye, making it much more severe and difficult to ignore.
2. Associated Symptoms
Headaches generally do not come with additional symptoms apart from the pain itself. They might cause some discomfort and distraction, but they typically don’t incapacitate you.
Migraine headaches, on the other hand, have additional symptoms that make migraines significantly more debilitating than regular headaches. These often force sufferers to retreat to a dark, quiet room to find relief and avoid further aggravation.
3. Presence of Aura
One of the distinguishing features of some migraines is the presence of an aura. Auras can involve visual disturbances like flashing lights, zigzag lines, or temporary vision loss.
Other sensory disturbances, such as tingling or numbness in the hands, face, or other parts of the body, can also occur.
Headaches do not have these auras, making this a key differentiator for diagnosing migraines and preparing for their onset.
How to Diagnose a Migraine VS Headache
Getting the right diagnosis is key to finding effective treatment. When you visit a healthcare provider to determine whether you’re experiencing migraines or headaches, they will usually do the following for a diagnosis:
- Neurological Examination: This helps to rule out other potential causes of your headaches.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans might be used to detect any abnormalities in your brain.
- Blood Tests: These tests can check for underlying conditions that might be causing your headaches.
Working closely with your healthcare provider helps ensure you receive the appropriate diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Treatment Options
Whether you’re dealing with a migraine or a headache, there are various treatment options available to help manage and alleviate your symptoms with over-the-counter treatments.
Headaches
Most headaches can be alleviated with over-the-counter treatments. These can include analgesics like ibuprofen, acetaminophen, and aspirin.
For more severe headaches or those that do not respond to over-the-counter medications, prescription drugs, like triptans or ergotamines, may be required.
There are also non-drug treatment alternatives like stress management techniques, regular physical activity, proper hydration, and adequate sleep. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and biofeedback can also be effective.
Migraines
Migraine attacks often require more specific prescription medications, such as triptans, which help to constrict blood vessels and reduce inflammation. Preventive medications like beta-blockers, antidepressants, or anti-seizure drugs may also be prescribed for chronic migraines.
Non-pharmacological treatments like lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, eating regular meals, and managing stress, can help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
Alternative therapies like acupuncture, biofeedback, and dietary supplements (e.g., magnesium and riboflavin) have also shown promise in managing migraines.
When to Seek Medical Help
Some warning signs necessitate immediate medical attention, including:
- A sudden, severe headache (often described as “the worst headache of my life”).
- Headaches that are accompanied by fever, stiff neck, confusion, or seizures.
- A persistent headache after a head injury.
- New, frequent, and severe headaches in individuals over 50.

Living With Migraines and Chronic Headaches?
Living with migraines, chronic headaches, and chronic migraine can be challenging. In fact, chronic migraines are considered the second-most cause of disability among young women.
If you battle chronic headaches or migraines, there are ways to lessen the global impact severity of these conditions.
For one, tracking symptoms and triggers can provide invaluable information for healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans effectively.
Moreover, patients with migraines and chronic headaches can contribute to advancing medical research by participating in clinical trials.
Clinical trials are safe, carefully executed research studies that test new treatments or approaches to prevent, detect, or manage diseases. They are essential for developing new therapies and improving existing ones.
Are you interested in contributing to research on chronic headaches or migraines? Then you’ve come to the right place.
Get Matched With Tandem Clinical Today
There are currently no cures for chronic headaches or migraines, but that doesn’t mean we can’t advance our understanding and treatment of these conditions.
Tandem Clinical Research wants to expand on the scientific research behind these common ailments. We match patients with appropriate clinical trials, offering hope for better treatments and outcomes. Most recently, we’ve been connecting female patients with clinical trials for menstrual migraines.
If you suffer from this type of migraine, contact us today to learn if you’re a candidate for a local study. Together, we can contribute to the latest research and help current and future generations battle this condition.
